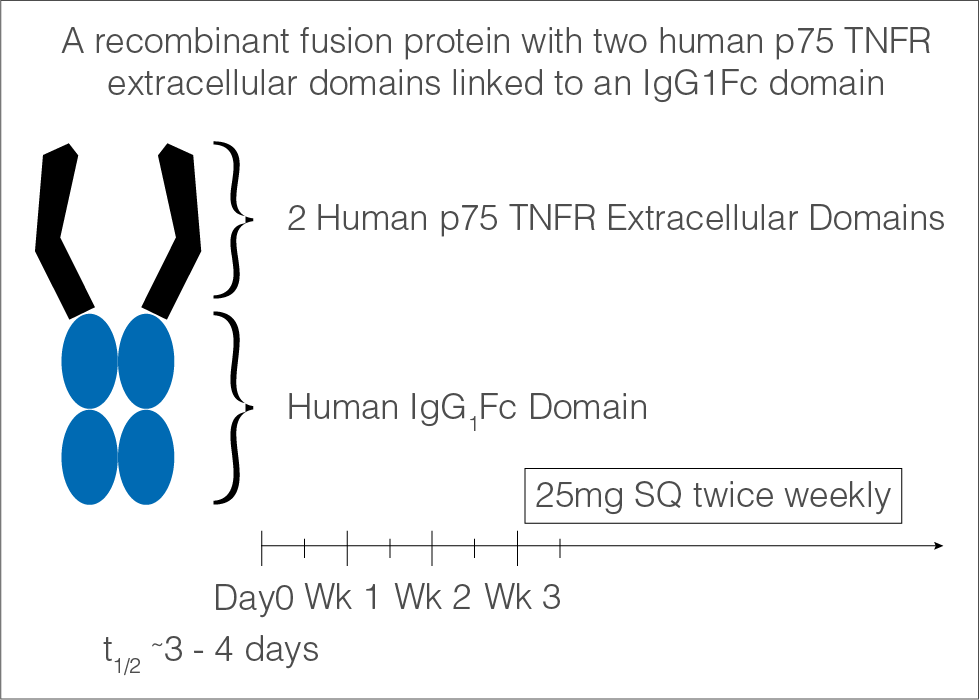
Etanercept only TNF blocker commercially available consisting in a fusion protein
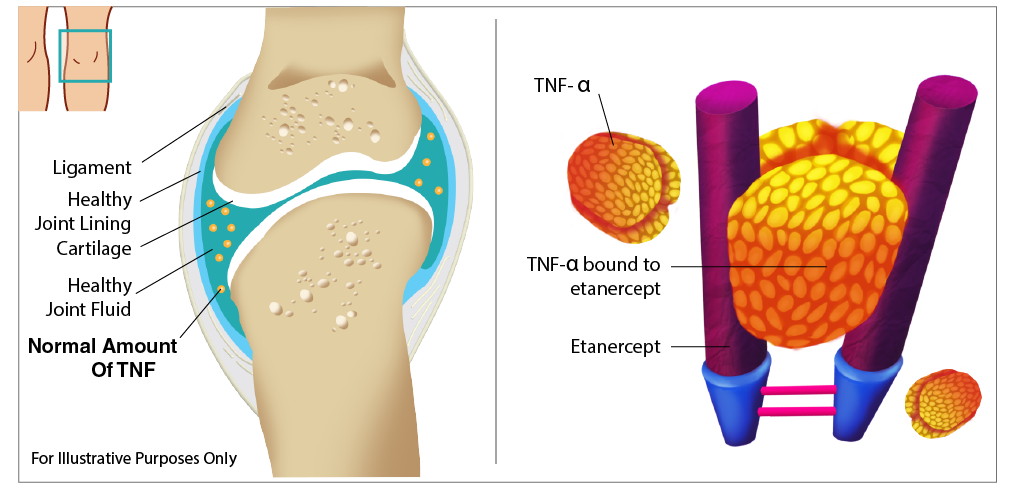
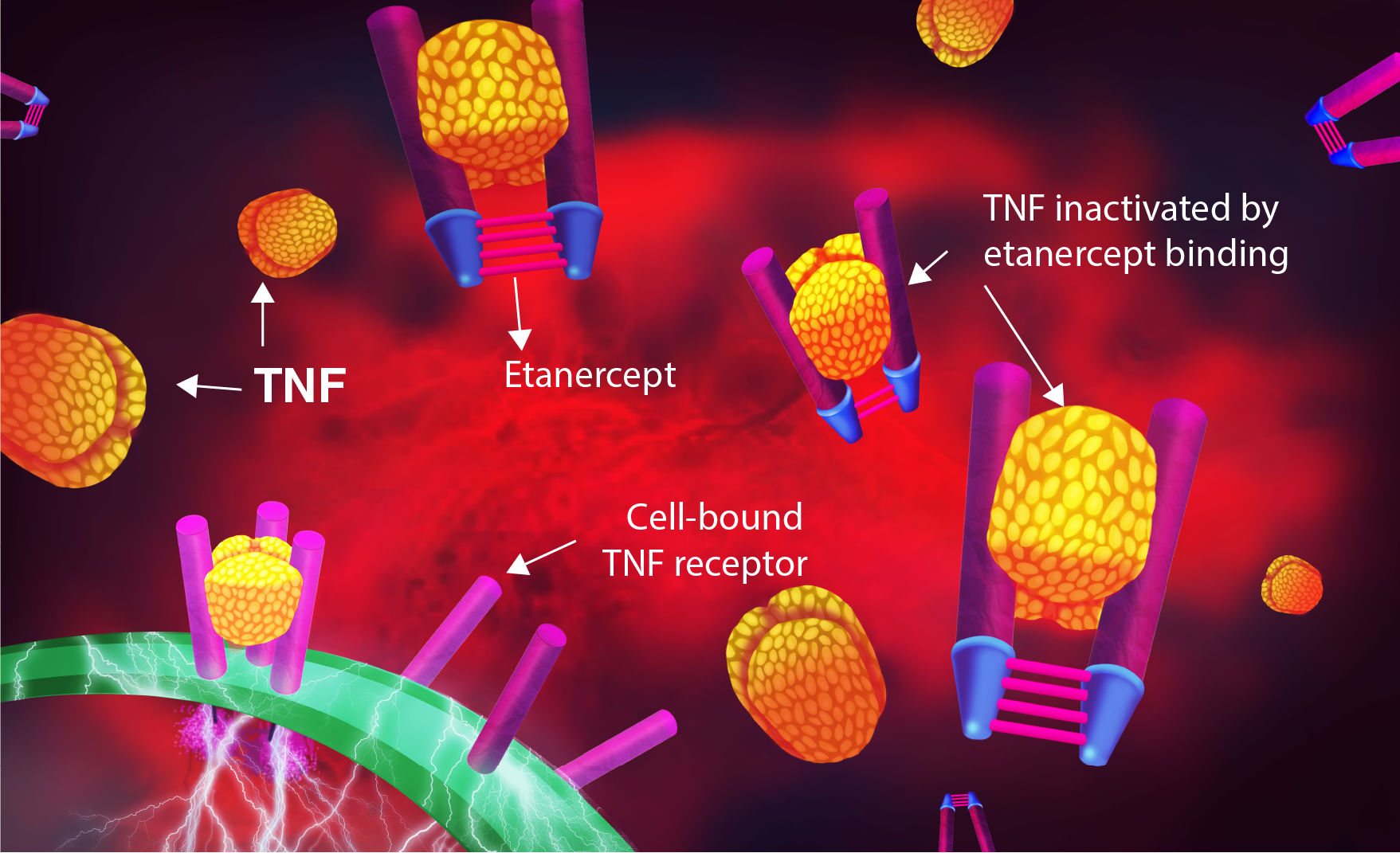
Autoimmune diseases are caused by an overactive immune response. TNF-alpha helps the body fight infection and cancer, but when over produced it can have harmful effects. TNF-alpha is main regulator of the inflammatory (immune) response in many organ systems. Over-production of TNF occurs in several diseases including Rheumatoid Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, Plaque Psoriasis, Psoriatic Arthritis & Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis, so anti-TNF drugs have been used as treatment. Tumor necrosis factor plays an important role in both normal immune function, and the cascade of reactions that cause the inflammatory process of RA, AS and psoriatic arthritis. Etanercept has the potential to treat these diseases by inhibiting TNF-alpha. Etanercept blocks the effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) so it is called an ‘anti-TNF’ drug. Etanercept binds specifically to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and blocks its interaction with cell surface TNF receptors. The binding of Etanercept to TNF biologically inactivates the bound TNF, resulting in a significant reduction in inflammatory activity.
WHY CHOOSE ETANERCEPT?
The Fc fragment prolongs the half-life of the compound in the bloodstream, therefore, with a more profound and long-lasting biologic effect than a naturally occurring soluble TNF receptor
The major side effect of TNF blockers is infection. However, Etanercept: lower incidence of tuberculosis; when compared to infliximab and adalimumab
Better maintenance rate with etanercept than for infliximab
The development of anti-drug antibodies (ADAb) formation was significantly associated with poor rates, but etanercept appeared to be less immunogenic and lack of development of ADAb