Subcutaneous Etanercept (10 mg or 25 mg, twice weekly) in comparison to Oral Methotrexate (19 mg per week) in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis
Study design
A study was conducted to compare the efficacy and safety of Etanercept and Methotrexate in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. A total of 632 patients with early rheumatoid arthritis were randomly assigned to receive either subcutaneous injections of Etanercept twice weekly (10 mg or 25 mg) or Oral Methotrexate per week (19 mg) for 12 months. Sharp scale was used to measure bone erosion and joint space narrowing. Clinical response was defined by the percentage improvement in the disease activity (the American College of Rheumatology [ACR-N] criteria).
Improvement with Etanercept and Methotrexate
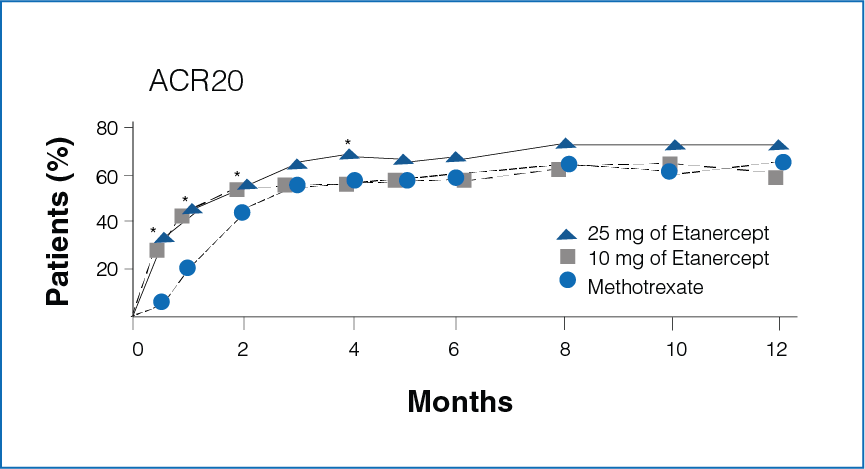
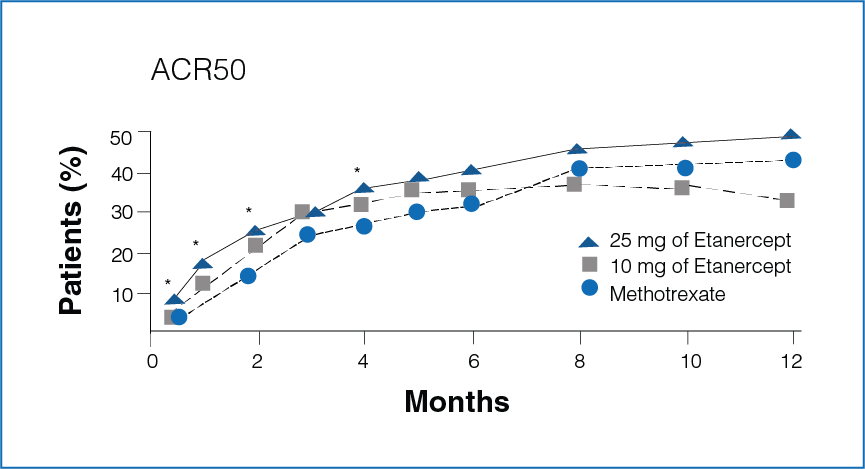
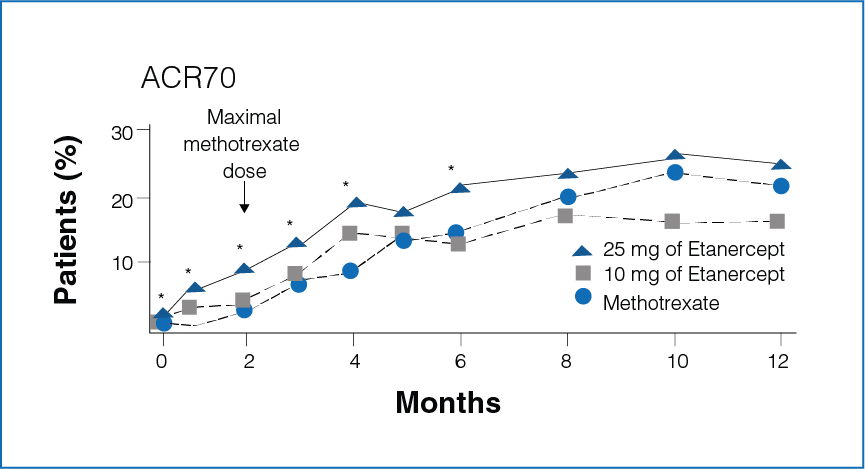
Figure 1: Percentage improvement with Etanercept (10 mg or 25 mg) and Methotrexate
*Significant differences between the Methotrexate group and the Etanercept 25 mg group (P<0.05).
- Rapid improvement was seen in patients receiving Etanercept 25 mg as compared to Methotrexate.
- Significantly more number of patients in the Etanercept-treated group showed 20%, 50%, and 70% improvement in disease activity during the first 6 months (P < 0.05, Figure 1).
Treatment effect
Figure 2: Mean response to Etanercept (10 mg or 25 mg) and Methotrexate from baseline
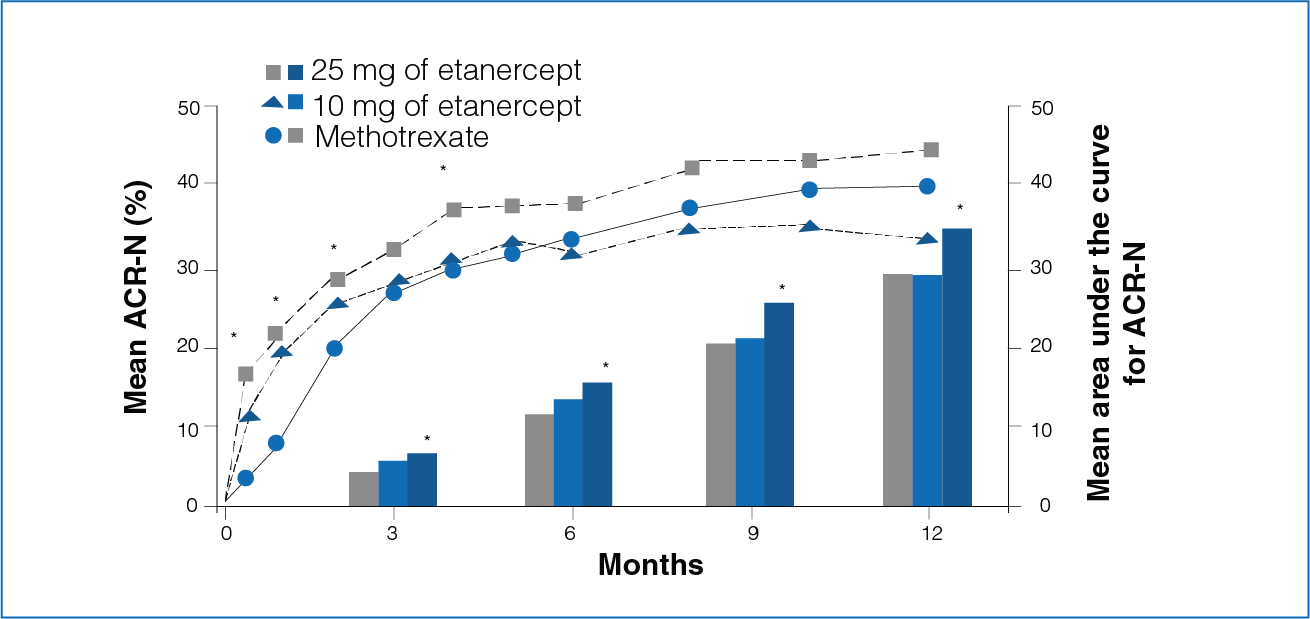
*Significant differences between the Methotrexate group and the Etanercept group 25 mg (P < 0.05)
*Significant differences between the two Etanercept groups (10 mg and 25 mg, P < 0.05)
Clinical response was defined by the percentage improvement in the disease activity (ACR-N criteria) and by the area under the curve for ACR-N.
- Rapid treatment effect was seen with Etanercept.
- The area under curve for ACR-N for 3, 6, 9, and 12 months was significantly greater in patients receiving Etanercept 25 mg compared to patients receiving Methotrexate (Figure 2).
Erosion score with Etanercept and Methotrexate
Figure 3: Mean change from baseline in the erosion scores at 6 and 12 months with Etanercept (10 mg or 25 mg) and Methotrexate.
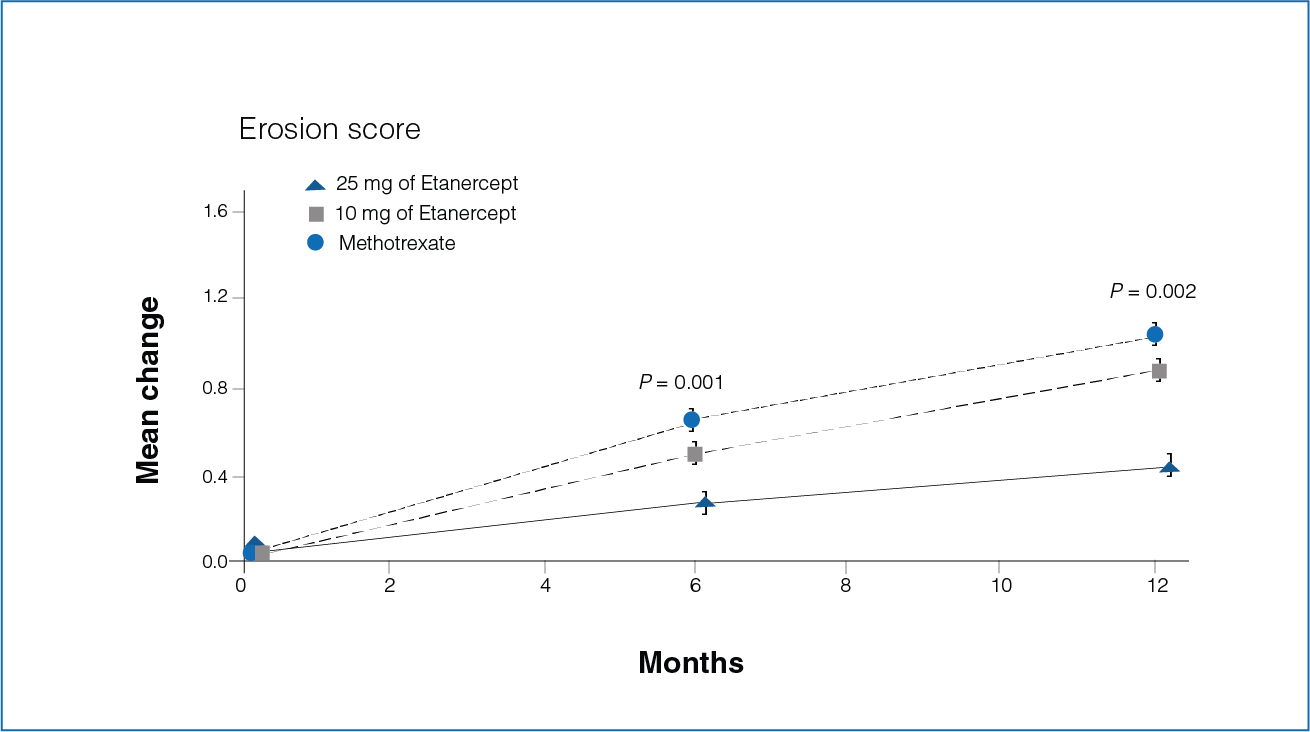
- Seventy-two percent of the patients in the Etanercept 25 mg group showed no increase in erosion score compared with 60% of the patients in the Methotrexate group (P = 0.007).
- The mean increase in the erosion score was 0.30 in the Etanercept 25 mg group and 0.68 in the Methotrexate group during the first 6 months (P = 0.001, Figure 3).
- The increase in the erosion score was 0.47 and 1.03 in patients receiving Etanercept 25 mg and Methotrexate, respectively, during the first 12 months (P = 0.002, Figure 3).
Safety Profile
- Significantly more patients receiving Methotrexate had adverse events as compared to patients receiving 10 mg Etanercept (P = 0.04) or 25 mg Etanercept (P = 0.02).
- The infections were significantly higher among patients in Methotrexate group compared with patients in the Etanercept group (P = 0.006).
Conclusion
As compared to Oral Methotrexate, Etanercept alleviates symptoms and slows down joint damage by acting more rapidly in patients with early active rheumatoid arthritis. The safety and tolerability profile of Etanercept in patients with early active rheumatoid arthritis was comparable to patients with long-standing disease.
Reference
Bathon JM, Martin RW, Fleischmann RM, Tesser JR, Schiff MH, Keystone EC, et al. A comparison of Etanercept and methotrexate in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2000 Nov 30;343(22):1586–93.
YISAIPU (Etveza) VERSUS REFERENCE BIOLOGIC ETANERCEPT
Statistical Comparative Analysis of the Efficacy and Safety of Yisaipu (Etveza) and Reference Biologic Etanercept
Treatment with Yisaipu (Etveza) in comparison to reference biologic Etanercept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Study design
A comparison analysis was done to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Yisaipu (Etveza) and reference biologic Etanercept from published data or the clinical study report. The data analysis in both trials was done based on the Intention to Treat (ITT) datasets, where participants receiving at least one dose of the study drug (Yisaipu (Etveza) versus reference biologic Etanercept) were included. The safety analysis in both trials was conducted based on the safety datasets, where participants receiving at least one dose of the study drug were included. The reference biologic Etanercept trial had 12-month safety data, while the Yisaipu (Etveza) trial had 6-month safety data.
The primary endpoint includes the percentage of patients who showed improvement of 20 percent (ACR20) at 6 months.
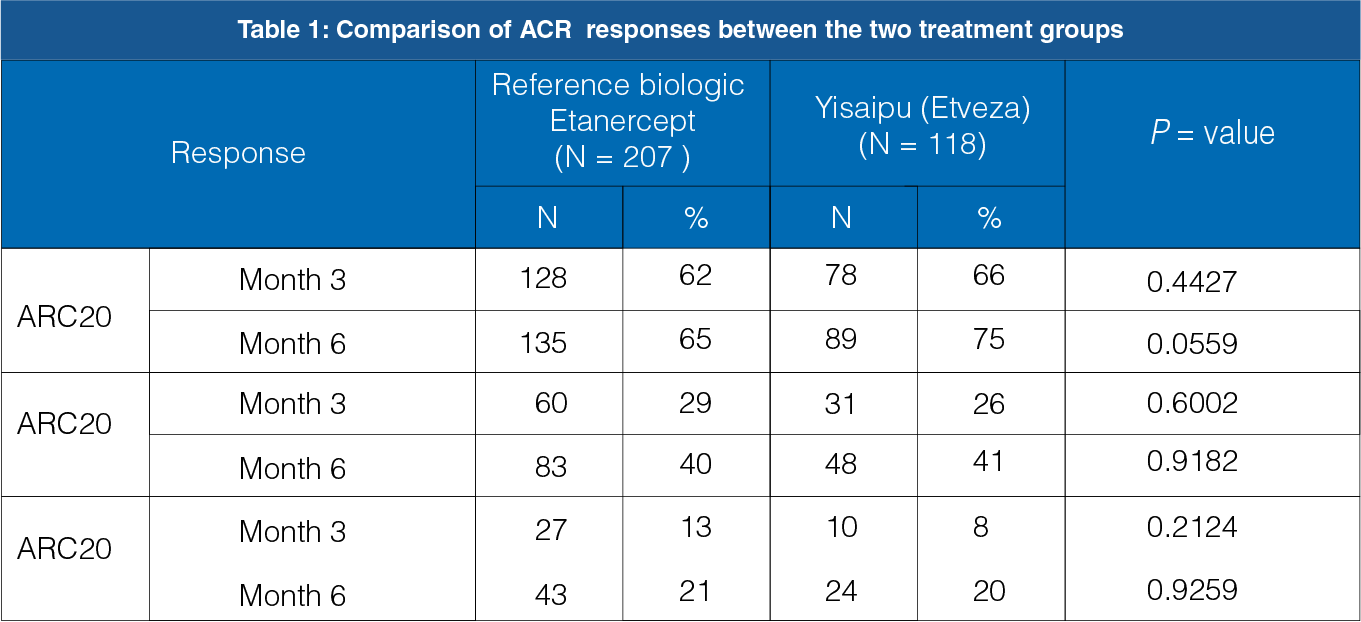
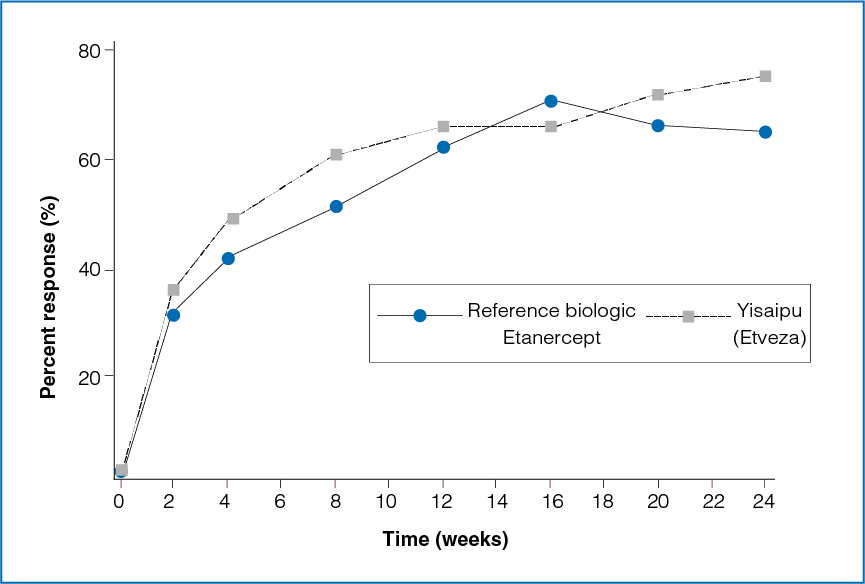
Figure 1: Time course of ACR20 response between the two treatment groups
The ACR20 response between the reference biologic Etanercept group and the Yisaipu (Etveza) group was not statistically significant at the end of 3 months (P = 0.4427) and 6 months (P = 0.0559, Table 1 and Figure 1).
The secondary endpoint includes the percentage of patients who showed improvement of 50 percent (ACR50) and 70 percent (ACR70) at 6 months.
Figure 2: Time course of ACR50 response between the two treatment groups
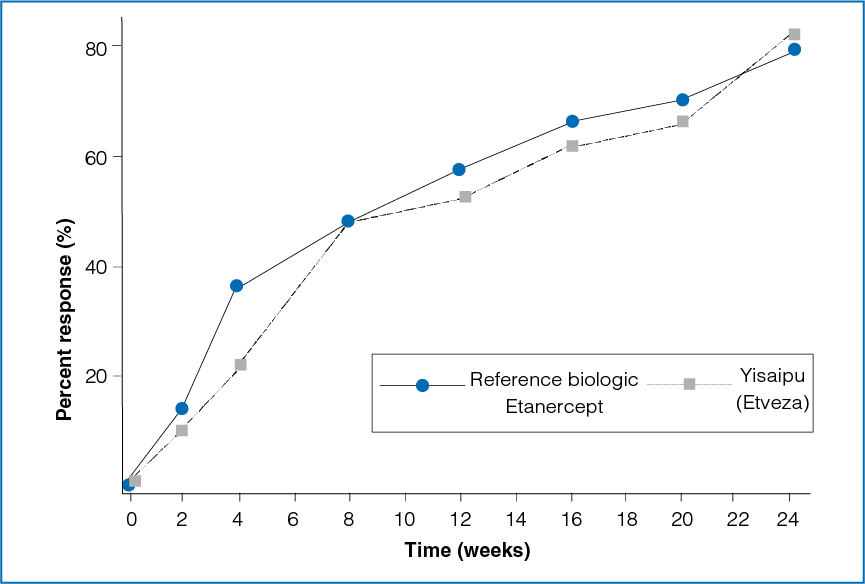
Figure 3: Time course of ACR70 response between the two treatment groups

The ACR50 and ACR70 responses between the reference biologic etanercept group and the yisaipu group were not statistically significant at the end of 3 months and 6 months (Table 1, Figure 2 and 3).
Safety profile
Commonly occurred adverse events in both intervention groups:
Reaction at injection site, upper respiratory tract infection & rash
Adverse events during the 12 months treatment in the reference biologic Etanercept group:
Headache, nausea, rhinitis, bleeding at injection site, skin infection, asthenia, influenza-like syndrome, dyspepsia, dizziness, back pain, abdominal pain, sinusitis, ecchymosis, alopecia, and mouth ulcer.
Adverse events during the 6 months treatment in the Yisaipu (Etveza) group:
Non-upper respiratory infection, hematology abnormality, liver function abnormality, gastroenteric symptoms, insomnia, swollen lymph node, constipation, blood pressure elevation, trichomadesis, chest stiffness, blurred vision, skin itching, poor eyesight, urinary calculus, hematuria & menorrhagia+
Conclusion
Statistical comparative analysis results showed that Yisaipu (Etveza) and reference biologic Etanercept are comparable on the efficacy and safety.
Reference
Bathon JM, Martin RW, Fleischmann RM, Tesser JR, Schiff MH, Keystone EC, et al. A comparison of Etanercept and methotrexate in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2000 Nov 30;343(22):1586–93.
Dawei Hu. Study 301-024 Phase II Clinical Study Report of ehTNFR: Fc in Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. NA: NA, 2004. NA.
REFERENCE BIOLOGIC ETANERCEPT VERSUS ETANAR® (Etveza)
Comparison of Frequency of Anti-drug Antibody among Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Two Etanercept-containing Products
Reference biologic Etanercept in comparison to Etanar® (Etveza)
Study design
A study was conducted to determine the presence of antibodies against Etanercept in Colombian patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with either reference biologic Etanercept or a follow-on biologic Etanar (Etveza). A total of 32 patients with rheumatoid arthritis participated in the study. Of the 32 patients, 16 patients were treated with reference biologic Etanercept and16 patients were treated with Etanar® (Etveza). Clinical and laboratory data of these patients were collected, and serum sample was taken for anti-drug antibody (ADAb) analysis.
Duration of disease and treatment with reference biologic Etanercept and Etanar® (Etveza)
Figure 1: Disease duration with reference biologic Etanercept and Etanar® (Etveza)
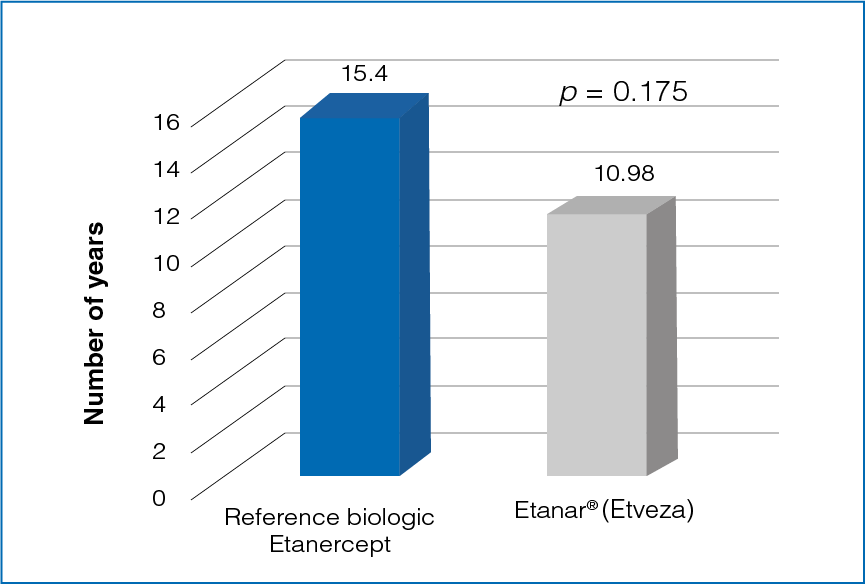
The duration of disease was longer in patients treated with reference biologic Etanercept than in patients being treated with Etanar® (Etveza) (Figure 1).
Figure 2: Average duration of treatment with reference biologic Etanercept and Etanar® (Etveza)
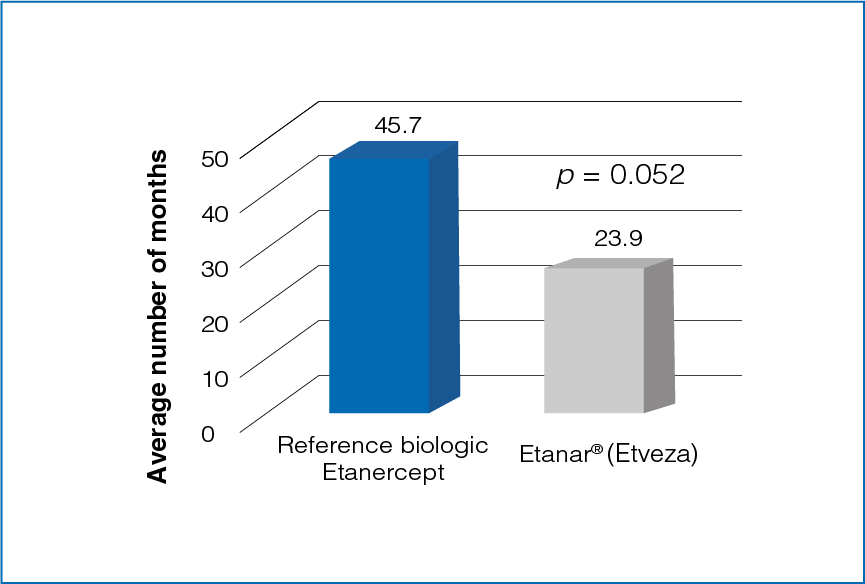
The average duration of treatment was longer for reference biologic Etanercept as compared to Etanar® (Etveza) (Figure 2).
Disease activity scores

- The disease activity score by erythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR) and disease activity score by C-reactive protein (DAS28-CRP) were higher in the Etanar® (Etveza) group than the reference biologic Etanercept group (Table 1).
- The difference between the groups was not significant.
Reactogenicity in ELISA among patients treated with reference biologic Etanercept and Etanar® (Etveza)
Figure 3: Reactogenicity in ELISA among samples from patients treated with reference biologic Etanercept and Etanar® (Etveza)
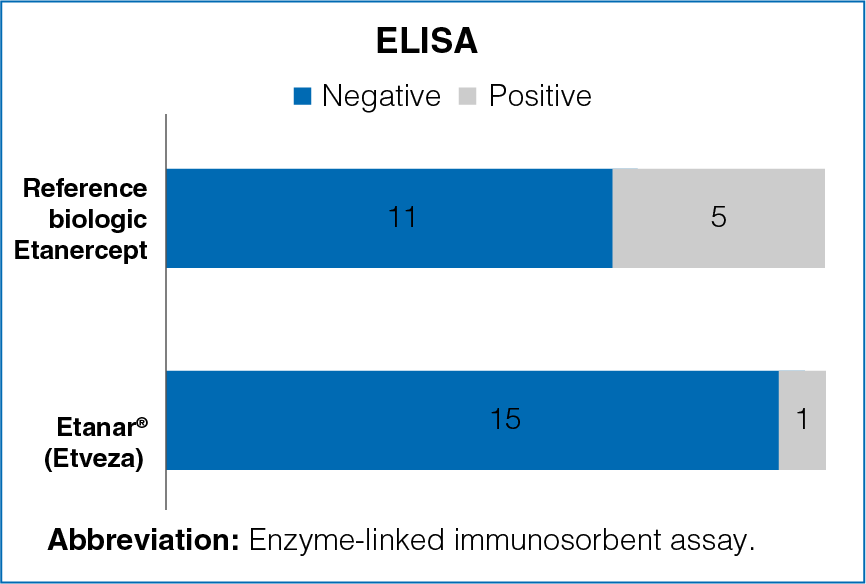
Positive sera for ADAb were found
- Positive sera for ADAb were found in 31.2% of the patients in the reference biologic Etanercept group and in 6.2% patients in the Etanar® (Etveza) group.
- The results were significantly different between the groups (Figure 3).

- In positive ELISA test group, the DAS28-ESR and DAS28-CRP scores were higher, although there was no statistically significant difference between the groups (Table 2).
Conclusion
- Based on the results of the ELISA assay, a greater frequency of ADAb was reported among patients treated with Etanercept than what has been reported earlier.
- Disease activity was found to be higher among patients tested positive for serum ADAb.
- With ELISA reactogenicity, significant differences were found between the sera of the patients treated with reference biologic Etanercept and those treated with Etanar® (Etveza).
- The length of the treatment time with the drug, the available commercial ELISA kit, or the immunogenicity of each product are some of the factors that could explain the differences between the sera from the patients treated with reference biologic Etanercept and that from the ones treated with Etanar® (Etveza).
Reference
Reyes-Beltrán B, Delgado G. Anti-drug antibodies in Colombian patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with Enbrel vs Etanar - Preliminary report. J Immunotoxicol. 2017 Dec;14(1):103–8.