Treatment with Etanar® (Etveza) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Study design
A 20-week multicenter observational before-after study was conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Etanar® (Etveza) in patients with long-standing, multiple disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)-resistant rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in a real-life setting.
About 110 patients with active RA were initiated on Etanar® (Etveza) treatment (25 mg subcutaneous injection twice per week) despite treatment with DMARDs. The patients were followed for a period of 20 weeks. The demographics and clinical characteristics, like health assessment questionnaire (HAQ) and disease activity score (DAS28), were recorded every 4 weeks.
Improvement in tenderness joint score and swollen joint score at follow-up
Table 1: Tenderness joint score and swollen joint score during follow-up

Significant improvement was observed in patients treated with Etanar® (Etveza) (P < 0.001,Table 1).
Improvement in disease activity score and health assessment questionnaire
- Reduction from 5.76 ± 0.81 to 3.48 ± 1.12 was observed in DAS28 (P < 0.001, by Friedman test) during follow up.
- At the follow-up period, a decline from 2.5 ± 1.1 to 1.1 ± 0.9 was seen in HAQ (P < 0.001).
Safety Profile
- Side effects were recorded in 10% of the patients.
- Lack of efficacy (n = 2), heart failure (n = 2), nausea and dizziness (n = 2), pneumonia (n = 2), and asthma (n = 1) were the main causes of discontinuation of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy.
Conclusion
Etanar®(Etveza) may be effective in controlling disease activity in real-life patients with active RA where MTX and other DMARDS show poor responses. Etanar®(Etveza) is safe and well tolerated.
Reference
Rondon F, Bautista A, Salazar JC, Casas N, Santos P, Vargas F, et al. Etanar (Etveza) therapy in real-life patients with rheumatoid arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(Suppl 10):1811.
Direct Comparative Effectiveness between Adalimumab, Infliximab, and Etanar® (Etveza) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Study design
The study aimed to compare the efficacy of two classical anti-tumor necrosis factor biologics (adalimumab, infliximab) and one Etanercept biosimilar in patients with long-standing rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in a real-life setting. A total of 158 patients with RA were assigned to receive adalimumab, infliximab, and Etanercept biosimilar Etanar® (Etveza).
According to the disease activity score (DAS28), the clinical follow-up was designed as follows:
- Every 3-5 weeks (DAS28 > 5.1)
- Every 7–9 weeks (DAS28 ≥ 3.1 and ≤ 5.1)
- Every 11–13 weeks (DAS28 < 3.1)
The treatment was adjusted with DAS28 > 3.2 unless patient’s conditions did not permit it (treat-to-target strategy; T2T). The patients were divided into two groups: the remission-low disease activity (Rem/LDA) and moderate-severe disease activity (MDA/SDA). The median DAS28 and the disease activity were analyzed using t-student distribution and Pearson's statistics, respectively.
Disease activity in the three treatment groups
Table 1: Disease activity at the start and 24-month follow-up
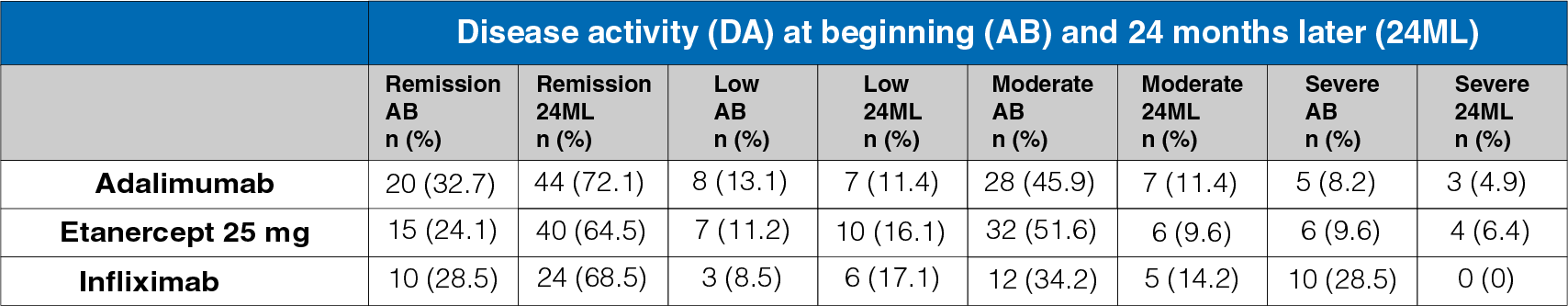
- A statistically significant increase was observed in the percentage of patients in remission at 24 months.
- A statistically significant decrease was observed in the percentage of patients with MDA/SDA disease activity (Table 1).
Improvement in disease activity score
- At 24 months, a decline in the DAS28 from 3.6 to 2.6 was observed in all the three groups.
- No statistically significant differences were observed between the three treatment groups.
Safety Profile
- Fewer adverse were observed with Etanercept biosimilar as compared to adalimumab and infliximab.
- The difference was statistically significant.
Conclusion
Etanar® (Etveza)- Etanercept biosimilar is as effective as adalimumab and infliximab in controlling disease activity in patients with RA in a real-life setting with fewer adverse events. The implementation of T2T strategy is effective in patients with RA.
Reference
Santos-Moreno P, Saavedra-Martinez G, Villarreal L, Gomez D, Bello-Gualtero J, Giraldo V, et al. Etanar (Etveza) – A Etanercept biosimilar is as effective as adalimumab and infliximab in a cohort of real-life of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74:789–90.
Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Etanar® (Etveza)
Treatment with 25 mg subcutaneous Etanercept [Etanar® (Etveza) 25 mg: biologic type rhTNFR:Fc] twice per week in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis
Study design
A study was conducted to evaluate the clinical response of patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with Etanar® (Etveza) (rhTNFR:Fc) at 12 month follow-up. A total of 105 patients with active rheumatoid arthritis were included in multicenter observational cohort study. The patients were treated with 25 mg subcutaneous Etanercept twice per week (Etanar® (Etveza) 25 mg approved for using in Colombia). The follow-up period of the study was 12 months, with assessments performed at weeks 12, 24, 36, and 48. The outcomes of the study included tender joint count (TJC), swollen joint count (SJC), health assessment questionnaire (HAQ), disease activity score 28 (DAS28), and American College of Rheumatology (ACR) response criteria (ACR20, ACR50, ACR70).
Improvement in TJC and SJC at 12-month follow-up
Figure 1: TJC and SJC at 12-month follow-up

- At the onset of study, the median of TJC and SJC was 19 and 14, respectively.
- At month 12, treatment with etanercept showed a progressive reduction in the counts, reaching a median of one for both TJC and SJC (Figure 1).
Clinical improvement with Etanercept at 12-month follow-up
The clinical response was defined by percentage improvement in disease activity (ACR-N criteria). The percentage of patients with at least a 20% improvement in the pain and edematous joint count, and in three of the five criteria (overall assessments by the doctor and patient, functional state, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate) were represented as ACR20. The threshold was also evaluated for 50% and 70% improvement (ACR50 and ACR70, respectively).
Figure 2: Percentage improvement with Etanercept at 12-month follow-up
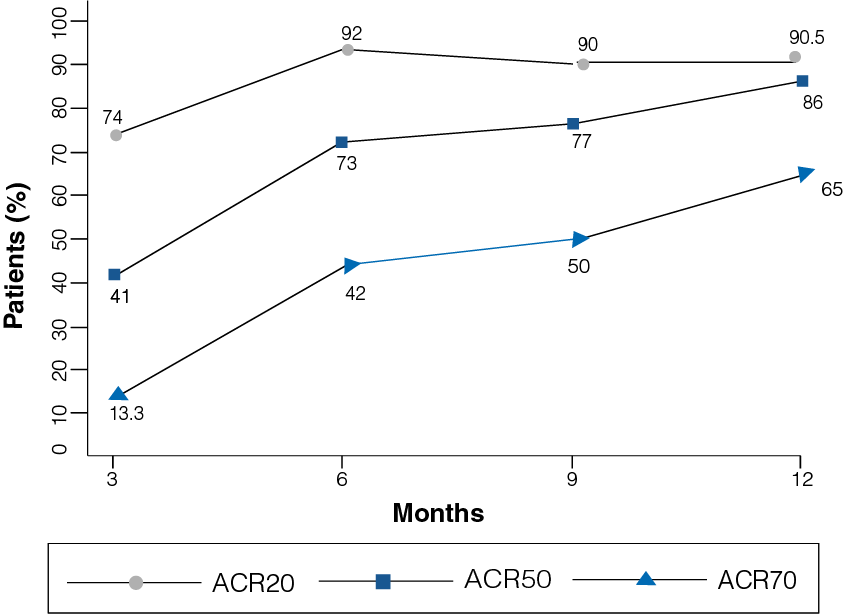
- A clinical improvement was observed in patients receiving Etanercept 25 mg.
- At 12-month follow-up, 90.5% of the patients reported ACR20 (p = 0.000), 86% of the patients reported ACR50, and 65% of the patients reported ACR70 (Figure 2).
Improvement in DAS28 and HAQ at 12-month follow-up
Figure 3: DAS28 and HAQ at 12-month follow-up

- Significant differences were observed in the DAS28 and HAQ throughout the follow-up (p = 0.000).
- At the onset of study, the median of DAS28 was 4.7 and reached 2 at the end of the study, while HAQ ranged from a median of 1.3 to 0.2 (Figure 3).
Safety Profile
- At the 12-month follow-up, 15 adverse events were reported (adverse events rate: 14 events per 100 people per year).
- No serious adverse events were reported during the study.
Conclusion
Etanercept 25 mg twice a week shows significant clinical results with adequate disease control in a high percentage of patients with adequate safety.
Reference
Reference: Santos-Moreno PI, Sánchez G, Gomez D, Castro C. Clinical outcomes in a cohort of Colombian patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with Etanar (Etveza), a new biologic type rhTNFR:Fc. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015 Nov-Dec;33(6):858–62.
Comparative Analysis of the Efficacy and Safety of Three Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Biologics in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Comparison of Etanercept [Etanar® (Etveza)], infliximab (Remecade®), and adalimumab (Humira®)
Study design
A observational retrospective cohort study was conducted to compare the clinical response and evaluate the adverse events in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with Etanercept, infliximab, or adalimumab at 36 months. A total of 307 patients with rheumatoid arthritis were assigned to receive subcutaneous Etanercept 25 mg twice a week (Etanar® (Etveza)), intravenous infliximab 3 mg/kg at weeks 0, 2, and 6 and then every 8 weeks (Remicade®), or subcutaneous adalimumab 40 mg every 2 weeks (Humira®). The follow-up period of the study was 36 months, with at least trimestral evaluations. The outcomes of the study included disease activity score 28 (DAS28) based on erythrocyte sedimentation rate for remission and low disease activity, health assessment questionnaire (HAQ), level of disability, and adverse events.
Disease activity score during 36 months follow-up
Figure 1: Median DAS28 from baseline to 36-month follow-up in the three treatment groups
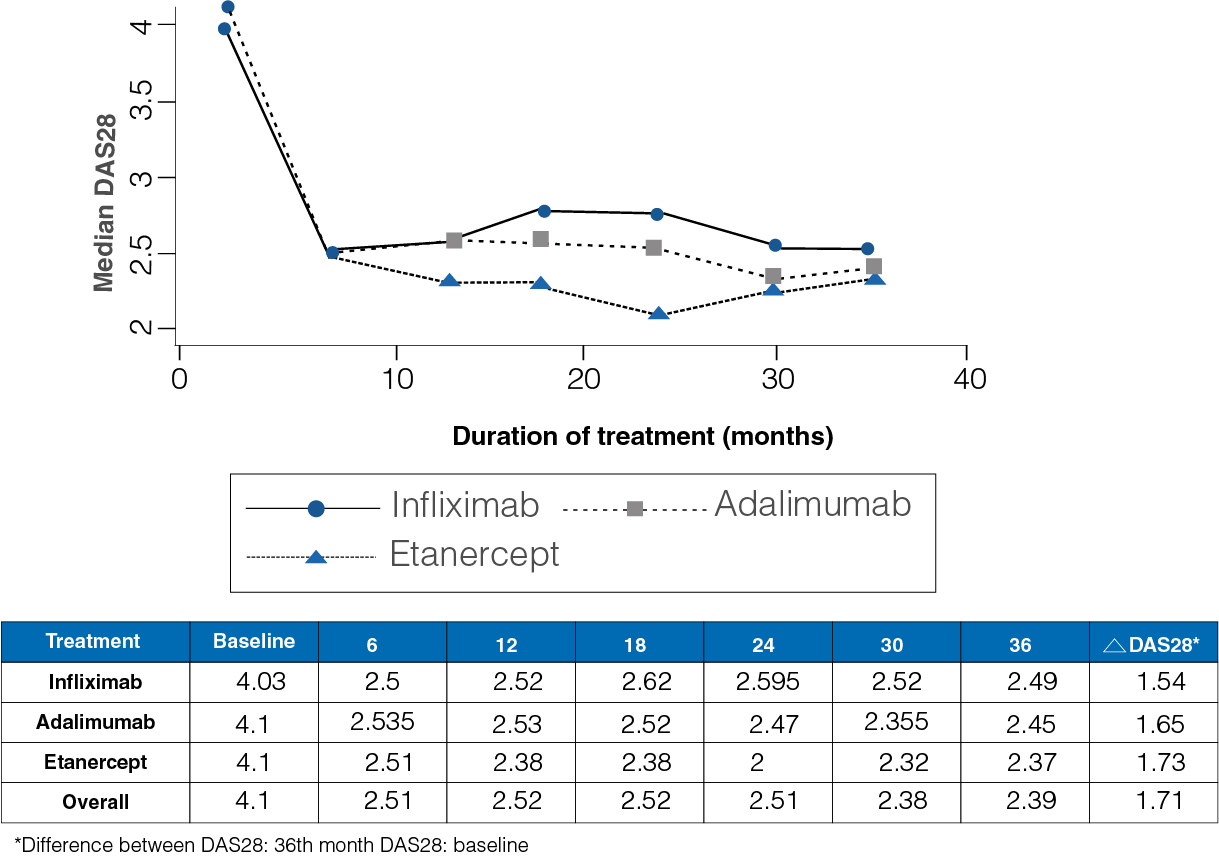
- At the start of the study, the median DAS28 was observed to be 4.1, and at the end of the 36-month follow-up period, it was 2.39 (Figure 1).
- A median difference of 1.16 for infliximab, 1.31 for adalimumab, and 1.38 for Etanercept was observed between the baseline and the end DAS28.
- No differences were observed between the three drugs (P = 0.51).
Level of disease activity
- The level of disease activity was analyzed based on the DAS28 outcomes along the follow-up.
- At the start of the study, a high disease level was seen in 25.7% of the patients, whereas at 36-month follow-up it reduced to 4.45% of the patients.
Remission rate
- A remission rate of 7.4 per 100 persons per month was observed, without differences between the treatment groups.
Improvement in health assessment questionnaire at follow-up
Figure 2: Median HAQ from baseline to 36-month follow-up in the three treatment groups
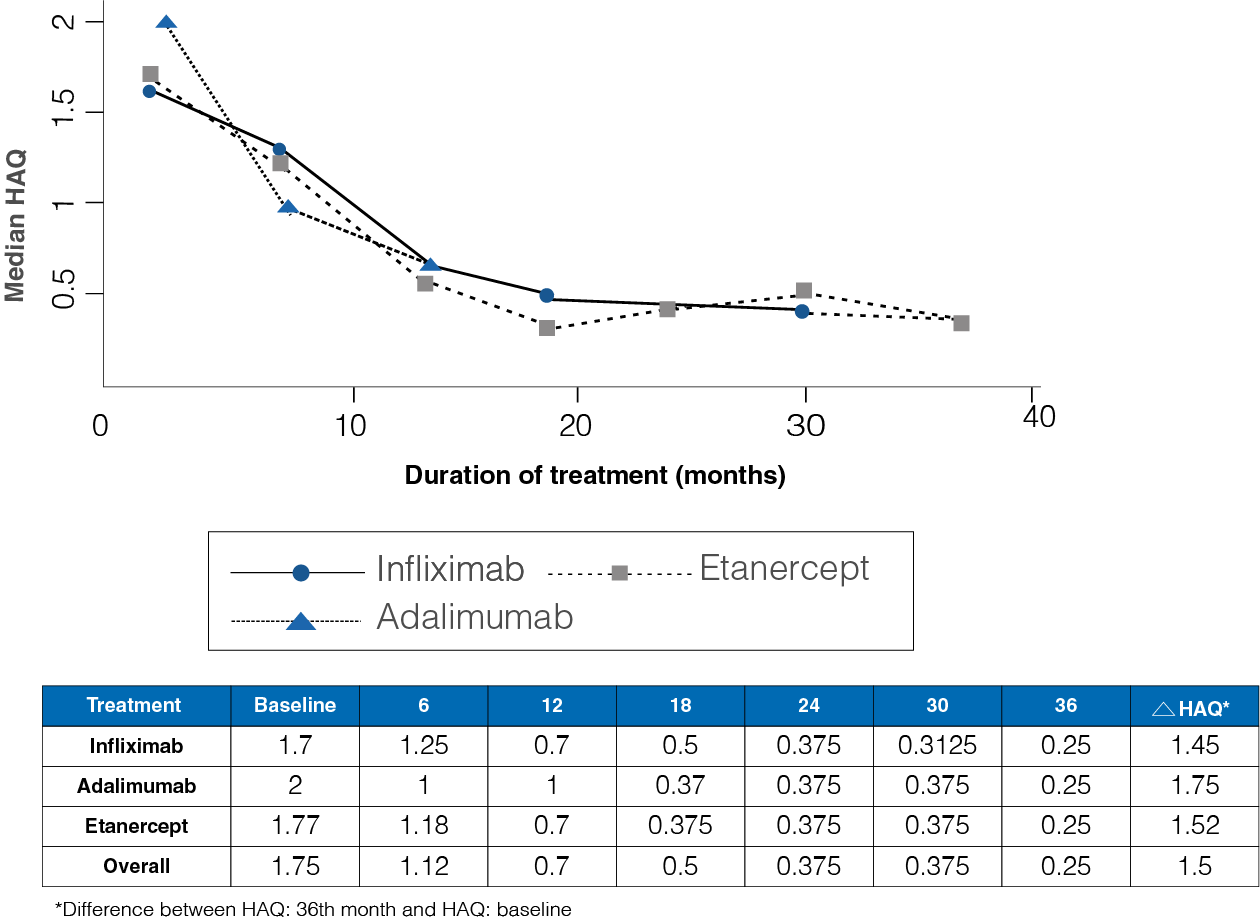
- The initial HAQ median was 1.75, while at 36 months the median was 0.25 (Figure 2).
- A median difference of 1.45 infliximab, 1.75 for adalimumab, and 1.52 for Etanercept was observed between the initial and final HAQ (P = 0.54).
Reduction in the degree of disability
Table 1: Level of disability during the 36-month follow-up in the three treatment groups
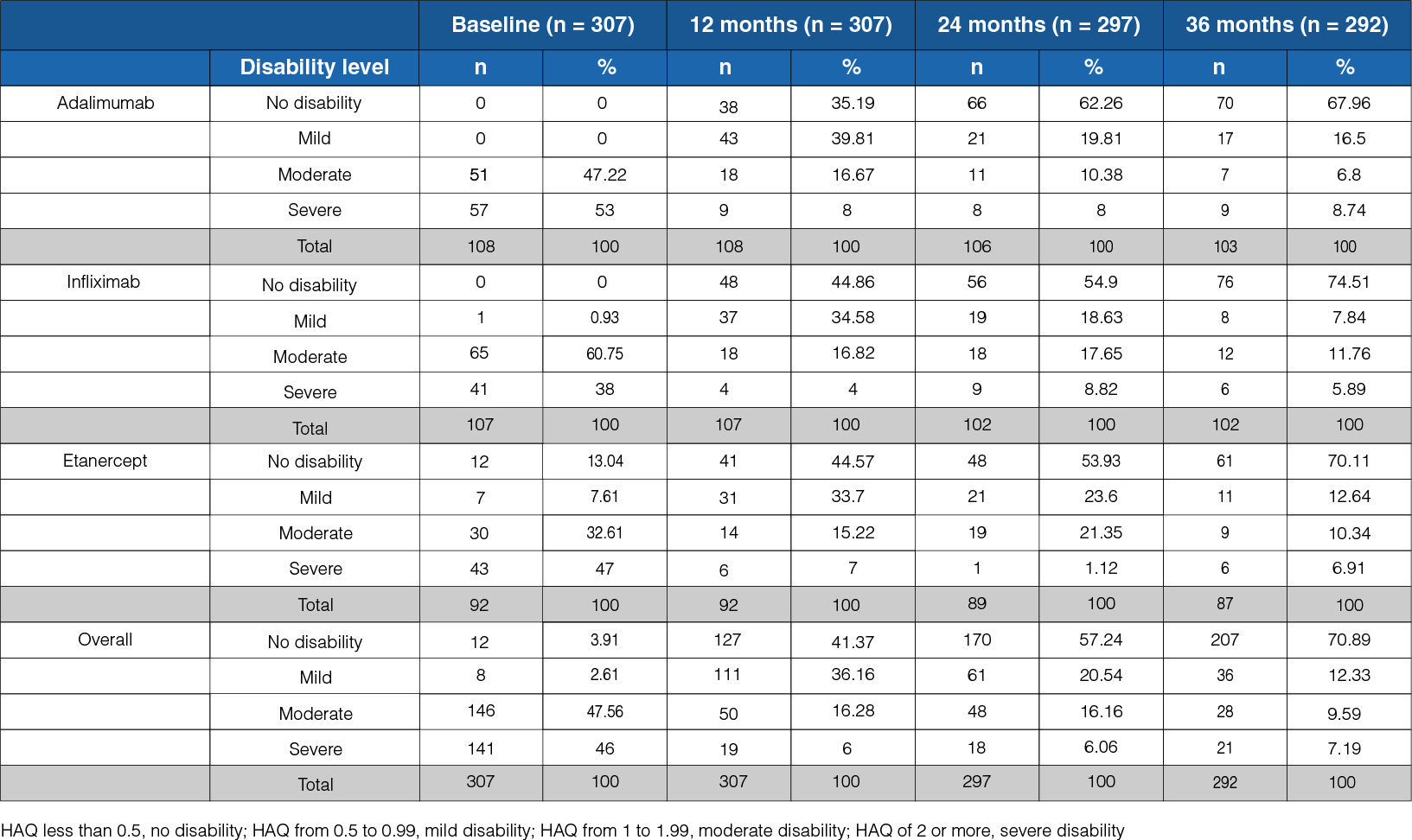
- At the onset, a severe level of disability was observed in 46% of the patients, whereas at the 36-month follow-up, it was observed in 7% of the patients (Table 1).
- At the follow-up, a state of no disability was seen in 71% of the patients.
Safety Profile
Table 2: Rates of adverse events in the three treatment groups during the follow-up
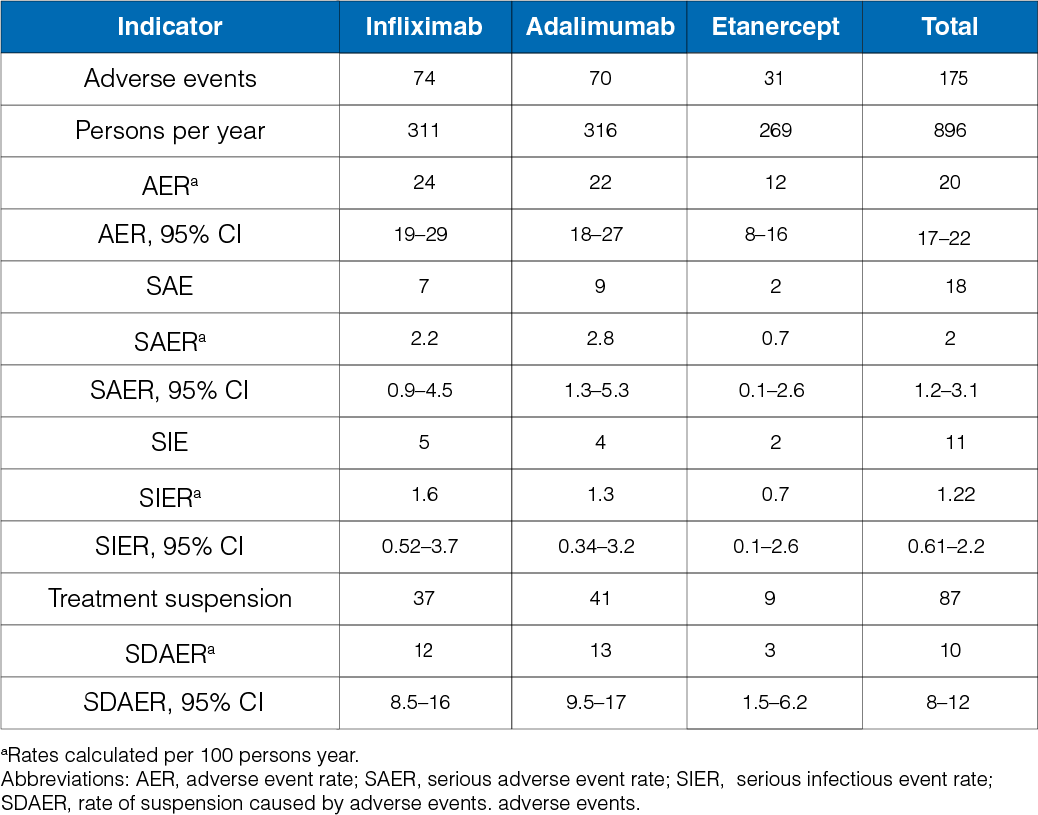
- The rate of adverse event was 20 per 100 persons per year. In the infliximab group, it was 24 events per 100 persons per year, whereas, in the adalimumab and Etanercept group, it was 22 events per 100 persons per year and 12 events per 100 persons per year (Table 2).
Conclusion
Etanercept, infliximab and adalimumab are effective therapeutic anti-tumor necrosis factor alternatives to reduce the disease severity levels and the degree of disability in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Etanercept shows lower rate of adverse events as compared to infliximab and adalimumab.
Reference
Santos-Moreno P, Sánchez G, Gómez D, Bello-Gualtero J, Castro C. Direct comparative effectiveness among 3 anti-tumor necrosis factor biologics in a real-Life cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Rheumatol. 2016 Mar;22(2):57–62.








